
So you have a product? Congrats.
There is only one problem: nobody gives a damn about your product unless people can find it. And nobody cares about Google search ranking when you don’t convert any significant part of that traffic.
Would you like your product to build more traffic and optimize conversion? It may be time to adjust your growth traffic strategy and read this SEO guide for inspiration.
This SEO guide focuses on providing quality content to gain the right traffic and build user confidence to buy your product.
Why SEO is hard
Money Ranking high in Google is equal to more traffic. And converting traffic means cash. Google knows that. That’s the reason why they place more advertising on top themselves (known as Adwords). Businesses pay top dollar for those ads. At the end of the day your salary depends on it.
Organic (SEO) traffic = scalable revenue.
Competition You’re not the only one who wants to rank on top. Google knows that. Google is looking for sites that give the best answers to the search queries of the user. The better your content is suited for the user, the higher you rank.
Machine learning Google introduced a new system behind their search engine called RankBrain. It’s a machine learning system that learns from what users search for and adapts the search results automatically. It means sites with better content can rank higher faster and results can change. Requiring consistent quality content production.
Requires consistent effort Automated SEO optimized content creation worked for some years. Google is paying more and more attention to user behavior on content (= SEO signals) and rewards those who put effort in giving users the best content possible.
Penalties for SEO ‘tricks’ Google doesn’t like to be messed with. Some SEO consultants will still jump on the ‘rank fast SEO’ bandwagon. Playing with forbidden methods can get you kicked out of search results with severe consequences.
Product revenue depends on it Unless you have millions in the bank, you just can’t run expensive ad campaigns. It’s therefor important to create a healthy marketing mix between paid and organic traffic. Investing in content can seem not so profitable in the beginning but it’s essential for long term sustainability for most online companies.
What you’ll learn in this SEO guide
How to structure your content operation for SEO. It’s not about ranking, it’s about providing the user with valuable content and building content in a consistent manner. Ranking is the result of that operation, not a goal by itself.
Prioritize content planning to create not only consistent but decide where to put your content resources. Google rather wants 10 top quality content pages than 1000 useless filled pages.
Understanding how certain SEO mechanics work so you have some more understanding what your SEO expert is actually talking about and therefor can make better decisions.
Planning
The first step in building for this SEO guide is planning. The goal of planning is mostly about deciding who and what to target.
Who is your audience?
This is the most fundamental question: who are you targeting? The answer to this question should already be answered. Most companies have mission/vision describing why they exist and who they serve. No SEO guide or trick will work when you don’t focus on the right audience.
My suggestion is to work with persona’s. Persona’s describe certain categories of people with their specific attributes.
The main question a persona answers: what goal does this type of user have and how is our product going to help them achieve their goal(s)?
Here is an example:
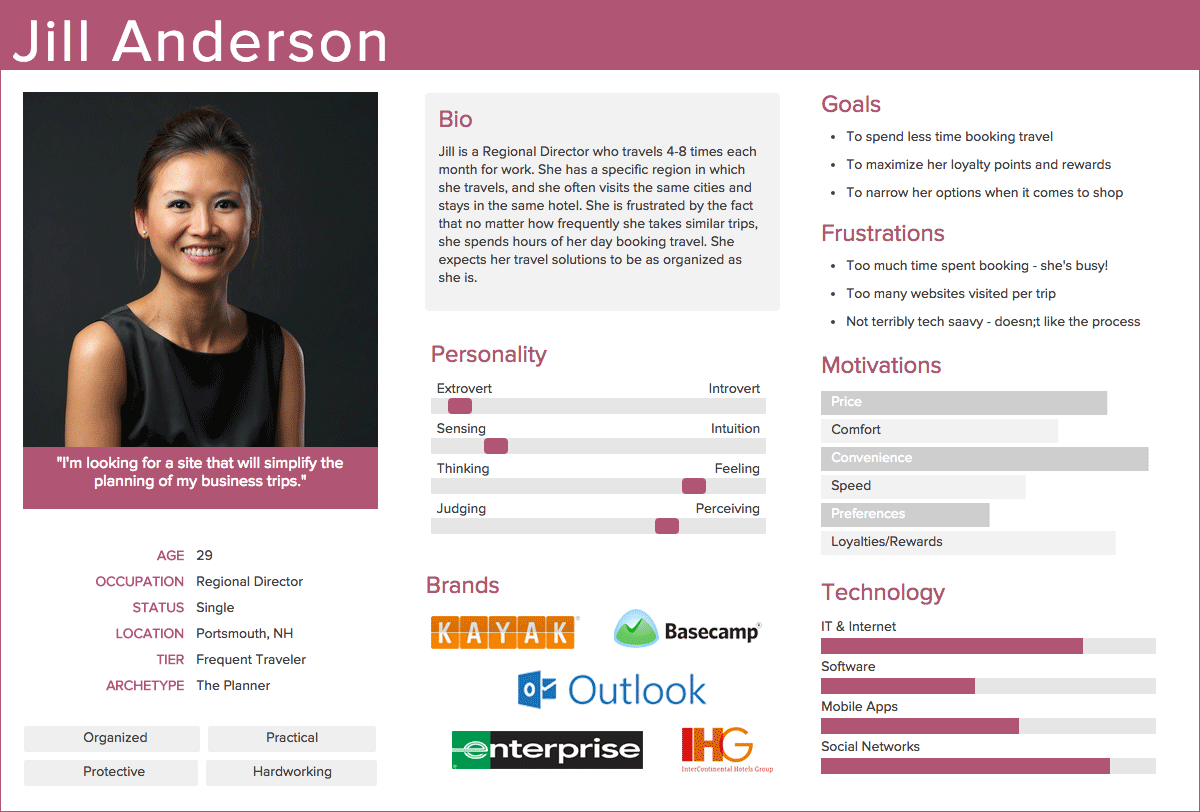
Where is your audience?
Your audience can be either on a specific platform, like Facebook. With a global audience it’s pretty standard to assume you have multiple channels your target audience can come from. You need to specify them and prioritize the importance of each channel. It will also give you more direction on what kind of content is suitable.
What content are they looking for?
Imagine your audience searching for content in Google. What keywords would they use? What answers are they looking for? Think about how you Google yourself. You just put in a few words and expect Google to get the answer. Your user expects you to be there when they type in their keywords. You need to figure out what words they use.
There are ways to get the answer while sitting at your desk. I’ll describe that in the section ‘Choosing search keywords’.
Do we have the resources?
Without creative people producing quality content, you can’t really beat any real competition. Content production needs sufficient resources.
Example: an in-depth article (like this one) can take a few days to write. You also need to factor in the required research, getting the right images, content approval, etc. It can add up fast.
The best way to determine resources is to first have a content plan and initial planning. Both are described below. Both pieces will answer how much people you’ll need to keep up your desired content production speed and quality.
Do you have a content plan?
Part of your own SEO guide is a content plan. If you never had heard of this before, don’t worry. This is mostly done by either the marketing or content department. It’s useful to be aware of. A content plan describes the following:
- Audience which you should’ve figured out by now. Most useful is to write them down in persona’s.
- Tone-of-voice Once you know who these people are, you need to decide how to address them. It runs down to using certain language to portray a certain tone towards your user. You need to describe this per channel. Communicating via e-mail can have a different tone-of-voice than via Twitter.
- The core message Whatever your write, it needs to have a clear message. What message should stick with the user after consuming your content?
- Content value Describe how content is actually constructed to make it valuable for the user. Make content for the user (worth sharing), not for your company. Which themes and subjects are relevant for us to produce content about?
- Roles who is responsible? You’ll be communicating content via different channels. It needs to be clear who has the lead and can make decisions.
- Timing describes how your content handles timing. How do you produce content that is time-sensitive (like news related)? It can also describe how to address urgent matters. For example bad press or negative responses on a review site.
Execution
By following the above, you should have a SEO gameplan. It’s time to turn words into action.
Choosing search keywords
As mentioned before, you need to imagine how your users search and what keywords they use. There are a fews ways to figure it out.
- Keyword planner is a tool by Google that gives you the search volume numbers of any keyword. You can find the keyword planner tool here. Here is a quick explanatory overview of what you’ll be looking at:

- Google trends is another tool from Google which focuses on trends for search keywords. The best feature is comparing keywords. For example: if I would run a hotel booking site, would it be better to focus on the singular keyword ‘hotel’ or the plural keyword ‘hotels’.

- Discover secret keywords Google doesn’t tell everything. Especially detailed keywords or niche keywords are good converting targets. So how do you find those? Well, there is a tool for that!
The end result should be a matrix of keywords you want to aim for. You can adjust it longer term once you get the hang of it.
Keyword matrix set, time to plan for content creation.
Content planning
Remember your content plan? Check the part that describes the content value and themes. Those themes should be the source of the subject lines that will eventually be your content posts.
Writing content means planning to write content. There a lot of content planning tools out there. Just try a few and pick the one your team is most comfortable with. A suggestion would be using Trello which is used within a lot of product teams.
Here is an example of the content planning in Trello within a tech company:

You can try this live demo for content planning yourself to get some look and feel experience.
Publishing content
Hooray! You finally made it to this section of the SEO guide. Which means you’re probably ready to show the world your beautifully crafted piece of content!
Just hold on for one moment and….
- Do some proofreading just like with making a product, it should be checked or tested by someone else first. Get someone to read the content to check its quality and meets the requirements from your content plan.
- Check if SEO proof There are actual tools that guide your writing content to be SEO proof. You can focus on creating content for your user while keeping an eye on how suitable it is for ranking. My personal favorite is this free content editor tool.
- Check your grammar slightly more important when you’re communicating on behalf of a company. Bad grammar can reflect badly on your company’s name. Tools like Grammarly can help you out.
- Choose the right channel(s) Some content is more suitable on Facebook, other content will be more suitable for Instagram. Pick your channels to distribute content wisely. Nobody is interested in your ‘spray and pray’ method. This will be bad for your conversion and only clutter your numbers.
- Reach out to blogs or sites to place a link to your content in a specific article or any relevant page that adds value to their user. This is referred to as link building.
Measuring
Now your content is out there. The last step is to measure how it’s performing. Content doesn’t only result in ranking and getting more domain authority, it also provides great learning lessons what your users like to see.
Measuring content performance
This SEO guide is full of nice free tools. This one may be the most important as you need to measure your actual SEO performance. It is a paid tool. If you’re serious about SEO, this will be money well spent.
After publishing content, it can take some weeks to actually rank (depending on your ranking authority at the point in time). One of my favorite SEO tools is SEO Powersuite. It gives you a full range of SEO insights.
The most important: how you rank on keywords

It gives you clear insights how your content is performing against your keyword matrix you already had. This will give you the feedback loop on data level to improve and adjust your keyword strategy.
Content iteration
Like code, content needs iteration overtime.You don’t have to iterate biweekly, just when you think it adds value to the user. Google actually looks for content that is refreshed once in a while. Some suggestions on refreshing content:
- New links If a post ranks and converts pretty well, it can be a valuable asset. You can add new external or internal links to improve the linking structure of your site. Another great opportunity is using the content within a partnership and give your partner exposure through your content.
- Update blocks Just a small section on top with updated info. It may also refer to content which is more relevant by date. This way you keep all the traffic of the content that already is ranking high and direct users who want the new content to the correct page.
Example of an update block:

Technical SEO
Here is the truth about SEO…
Without knowing anything about the technical stuff, SEO is a very hard game to win. The section of the SEO guide goes a bit deeper into some technical parts that are very useful to get your head around.
Most important: conversion
The end result of all your SEO content efforts should be converting traffic. Whether its content consumption for ad revenue or a visitor actually converting into a customer. It’s important to track those conversion events (like subscribing as a user).
The best way to do that is creating events in Google Event Tracking and build a proper funnel to see conversion metrics. The result should be looking like this:

….this is the reason why you want to master the art of conversion
The reason is not so much on the organic traffic side but on the paid traffic side. Once you want to advertise on top positions in Google Adwords, they’ll look at your conversion on clicks (CTR). The better you convert, the lower your advertising will cost.
Google rewards advertisers who have quality ads, it’s that simple. So you’re reward will be on both sides. More money in the bank!
Ranking authority
Ranking authority basically means how good your domain scores and acts as a SEO guide for your links ability to rank. This is mostly determined by a list of factors. But consistent original content and people referring to that content are the true basics of it.
Google will reward you with more authority if more people refer to your content. With more authority you’ll get a very important power: the ability to rank better and more links of your site on top position for (popular) search keywords.
Crawl budget
An important principle to understand from this SEO guide is crawl budget. Creating a lot of content and pushing it like some kind of factory won’t work. Google doesn’t actually consider all the links from your site when their bots index your site.
Crawl budget comes with ranking authority. It is basically like a financial budget for your department. You can spend X amount and that’s it. With crawl budget, you can only index X amount of links in Google search.
Google only considers your best pages, mostly the ones which are the most popular and least stale (= too static, no real updates or additional good content).
You can’t calculate your crawl budget upfront as Google doesn’t reveal any of that information. Google does tell you how many urls they indexed and can vary on your performance. You can keep track of it via Google Webmaster
It will be your SEO guide for link budget: It will look something like this:

Site structure: Internal vs external linking (backlinks)
The cornerstone of SEO: links. Linking to a page is for Google like voting: a link votes on a page or site to be of value to them. The more sites that link to your site, the higher you rank. This is not entirely true. Google doesn’t only look at the amount of external links pointing at you. It also looks what kind of sites link to you.
Example: if you’re a tech site about phone reviews and a lot of phone blogs link to you, Google assumes you apparently an authority in mobile phone reviews and will rank you higher with keywords in that specific area.
This most important thing to remember about links: only try to get quality backlinks, not as much links as possible.
When a lot of sketchy sites (like torrent sites or sites with illegal practices) point to you it’s called negative SEO. This will give you lower rank.
….then there is internal linking
Links within your site are almost equally important. Internal links are links that you put in your page to another page of the same site. Google sees them as votes as well. If you point a lot of links to a certain page within your site, Google knows that this specific page is important and will put it higher in priority to index and rank.
It is also valuable for a user reading content. You can add links to give the user more follow-up content, in-depth content or content that is associated by theme.
SEO signals
Google doesn’t guess how good you are, they measure. It looks at a few signals from user behavior to see if your content is any good and ranks your according to that behavior. Some important signals they watch for:
- Bounce rate the percentage of users who enter your site (from Google search) and leave on the same page. This signal indicates users couldn’t find what they were looking for. This way, Google determines how good your content answers the search request. Sometimes the first page actually answers everything. Google has another measuring weapon to cover that.
- Long clicks the average time a user sticks on your site page after clicking your link in Google search. This your users leaves your site after the first page but stick around pretty long, Google knows your content has value to the user. The average time based on my own experience is about 2-3 minutes. Most of the links from one of my own sites around that average time rank on top in Google.
I could fill this SEO guide with a dozen more SEO signals. Let’s keep it at this to focus on the most important. These two can be considered the most important. If people don’t like your content, it will reflect in these two SEO indicators.
Site speed
Everyone hates sites taking ages to load. Search engines measure your site speed and punish your ranking when your site is too slow. Google doesn’t rank on the fastest sites, just the speed required to not annoy users.
Google helps you figuring out if your site is slow and how to fix it with their website test tool.
Social media SEO
Google doesn’t neglect social networks. In fact, they use those as SEO signals as well. If people share your link on social networks, you can bet Google takes notice for ranking you higher.
Multiple studies have found similar importance of social networks as ranking factor for your SEO. It may in some cases be the most important factor:

SERP feature
SERP stands for Search Engine Result Page. SERP features are extra additional features you can add to the display of your link in the search results. These features are mostly only shown if you rank on top of the search results.
The main goal of SERP features is to show the user you are trustworthy, are an expert on your content and an authority in your field. This gives a higher probability of a user clicking on your link in the search results.
There are certain types of features you can use:
- Rich Snippets adds more visuals layer to the result (review stars for ratings).
- Universal Results additional information that displays with your result (mostly images or feature snippets of your page)
- Knowledge Graph those boxes that appear on the right in search results when a user is searching for certain popular entities (historical figures, celebrities, etc)
Example of a SERP feature:

Open Graph
There is another important channel you may have forgotten: messaging apps. People share links more and more via those apps like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Line, etc.
You probably have received a link like this:

Have you ever wondered how that link preview is made? Where does it get the picture from?
This is called Open Graph data and can be added to all your pages. It’s mostly auto-generated based on the content that’s already there on the page. It’s not only used by messaging apps. Almost every app and site that wants to generate an appealing preview of your content to their user.
It’s a great way to present your content in such way that a user WANTS to click on it.
Security
Users care more and more about security and so do search engines. Google has made no secret that providing your site via a secure (HTTPS) connection is now an actual ranking factor.
The good news is: the required certificate for providing a secure connection can be free! A lot of sites use a certificate called Let’s Encrypt. This SEO guide page and site are secured with the same certificate.
If you need more extended validation or authority based certificate, you have some paid SSL certificates options. If you’re site isn’t via secure connection, time to get it fixed.
Conclusion
I think it’s obvious to say: SEO is hard and requires a lot of effort. It takes planning, writing, publishing and iteration on a site-wide level to gain serious SEO ranking. Although can seem hard, it’s all about practice and experimenting with content that sets you apart from all others.
This SEO guide is just a quick overview of how to start and get to a consistent operation towards improving your SEO traffic and product conversion.
If you had a hard time on the technical SEO part, no sweat. That’s normal. Just read those definitions a few times and it will give you the understanding to go deeper into those mechanics.
Any suggestions to add to this SEO guide? Need more help with your product SEO or you have any question? Send me a message.



